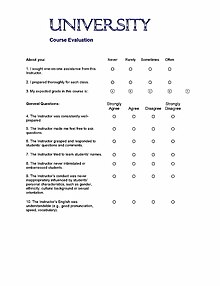
File Compression-> It is commonly used when sending a file from one computer to one another over a connection that has limited bandwidth. The compression is basically makes the files become smaller and therefore the sending of a file is usually fast and more better.
-> It is a hard disk failure that occurs when a read-write head of a hard disk drive comes in contact with its rotating plater, resulting in permanent and usually caused until fatal damage to the magnetic media to the platter surface.
Internet Hard Drive
-> Internet hard drive is about creating a new solution to the issue of data storage. The sole purpose of this is to offer a means of accessing your computer files from any computer. As long as your computer is access to Internet.
| Internet hard drive |
Optical Disk Drive
-> It is a disk that uses laser lights or electromagnetics waves near the light spectrum as part of the process
of reading and writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from discs, but recent drives are commonly for readers adn recorders.
 |
| CD-ROM drive. |
Solid-State storage
-> It is a method of data storage accomplished by using integrated circuit devices to store data rather than moving magnetic or optical media. SSS is typically non-volatile and may take various forms, such as solid state drive, solid state card or solid state module. In addition, SSS includes PATA(legacy), SATA, SAS, fibre channel, or PCIe interface options.
| Solid state storage |